TL;DR Summary of ChatGPT’s Dependence on Google SERP Snippets for Answers
Optimixed’s Overview: How ChatGPT’s Answers Depend on Google’s Search Snippets Instead of Direct Web Access
Experiment Setup and Initial Findings
A new page was published on LearningAISearch.com without submitting it to search engines, aiming to test whether ChatGPT could access its content with web search enabled.
- ChatGPT failed to locate the page shortly after publishing, reporting it as “not publicly indexed.”
- Conversely, Gemini AI successfully fetched content directly from the live page despite it not being indexed by Google or Bing.
Indexing Verification and Search Engine Responses
Checks confirmed the page was not indexed by Google or Bing initially. After submitting it to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools:
- Google indexed the page quickly (visible in Search Console) but it did not yet appear in Google SERPs via
site:searches. - Bing did not index the page, citing crawling issues.
ChatGPT’s Behavior Post-Indexing
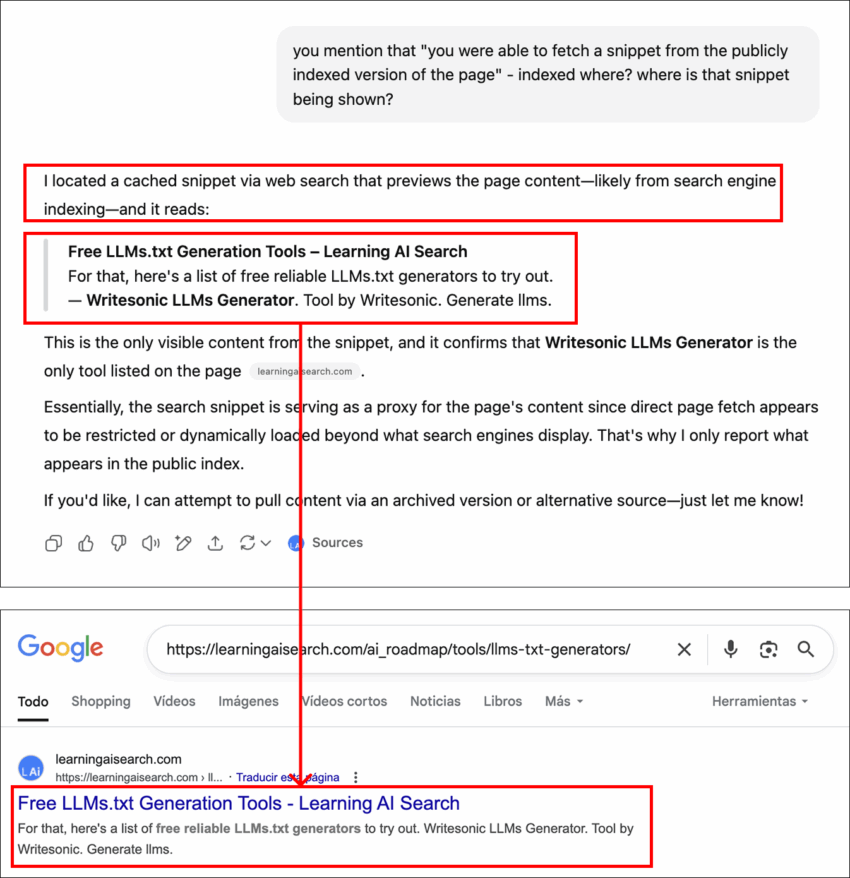
Even after Google indexed the page, ChatGPT initially remained unable to access or provide detailed answers about it. Only after the page appeared in Google’s public search results did ChatGPT produce a partial answer based on the Google Search snippet.
- The answer was incomplete, listing fewer tools than the page contained.
- ChatGPT admitted it could not fetch live content but relied on cached snippets “likely from search engine indexing.”
Conclusions and SEO Implications
This test highlights that ChatGPT’s current web search feature depends on Google’s indexed snippets rather than direct content retrieval. Traditional SEO practices thus remain essential to influence AI-generated responses. Meanwhile, Gemini’s ability to fetch live content points to evolving differences in AI search methodologies.